Hodgkin's Lymphoma- Keyword Analysis
Topics/keywords: ‘hodgkin’s lymphoma’
Data types: posts, comments, likes, polls
Geographical segment: global physicians, physicians by region
Analyzed data points on G-Med: 6,572
Specialties: Hematology, Oncology, Radiation Oncology, Internal Medicine
Countries analyzed: 65
Reach: 52,622
Introduction
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of physician discussions related to Hodgkin’s lymphoma, sourced exclusively from the G-Med platform. The analysis covers both unique posts and comments authored by physicians worldwide, with translations and standardization applied to non-English content. By applying keyword-based thematic mapping, frequency analysis, and sentiment breakdowns, we identify the most prominent clinical concerns and decision-making patterns. This includes physician perspectives on diagnosis, treatment, follow-up, and cross-country differences in approach.
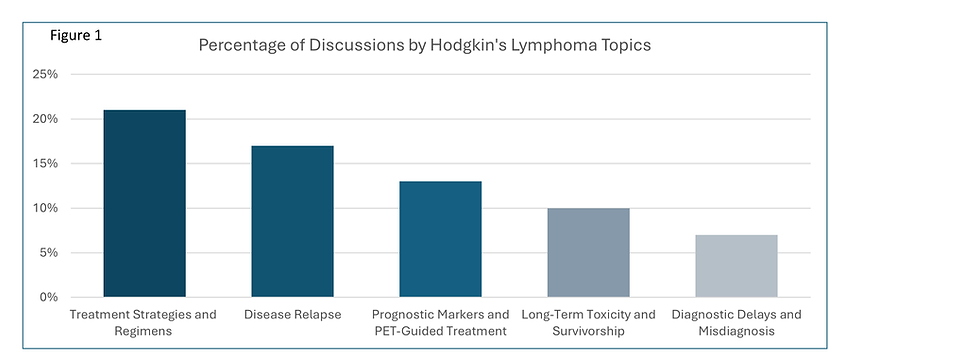
Main Concerns of G-Med Physicians on the Topic of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
.png)
· Treatment Strategies and Chemotherapy Regimens (21% of physician discussions)
Physicians widely discussed standard regimens such as ABVD and BEACOPP, as well as newer approaches like Brentuximab Vedotin combinations and checkpoint inhibitors for refractory cases.
o 61% expressed positive sentiment about ABVD as a reliable first-line option.
o 39% raised concerns about BEACOPP toxicity or overtreatment in early-stage patients.
· Disease Relapse and Refractory Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (17%)
There was strong engagement around how to manage relapsed or refractory cases, particularly regarding salvage chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation.
o 54% supported early salvage therapy followed by transplant.
o 46% expressed concern about timing, toxicity, or treatment fatigue in relapsed patients.
· Prognostic Markers and PET-Guided Treatment (13%)
Discussion focused on PET-CT scan interpretation, Deauville scores, and prognostic indices like the International Prognostic Score (IPS).
o 67% of posts favored PET-guided de-escalation strategies in favorable early-stage disease.
o 33% were more hesitant, citing inconsistent PET results or false positives.
· Long-Term Toxicity and Survivorship (10%)
Physicians noted concern over cardiotoxicity, secondary malignancies, and infertility from treatment.
o 72% expressed concern about long-term toxicity, especially in young patients.
o 28% reported using fertility preservation counseling or cardio-protective strategies.
· Diagnostic Delays and Misdiagnosis (7%)
Several posts highlighted missed early diagnosis due to nonspecific symptoms or misinterpretation of lymphadenopathy.
o 59% of physicians emphasized the need for early biopsy and imaging.
o 41% reflected frustration with delayed referrals or initial misdiagnoses.

Key Points on Diagnosis, Treatment, and Follow-Up

Diagnosis (18% of physician discussions)
Early Biopsy and Imaging: Strong consensus around the importance of excisional biopsy and PET-CT as first-line diagnostic tools.76% supported aggressive early diagnostic workups to avoid delays.
Misdiagnosis and Differential Diagnosis: Cases of Hodgkin’s lymphoma being mistaken for infections or autoimmune disease were noted, particularly in younger patients. 48% expressed concern over nonspecific presentations and overlapping symptoms.
Use of Molecular and Immunohistochemical Markers: Some discussions mentioned CD30, CD15, and PD-L1 as diagnostic and therapeutic targets.
Treatment (28% of physician discussions)
Chemotherapy Regimen Selection: The ABVD regimen was the most mentioned and positively viewed in 65% of treatment-related discussions. BEACOPP was reserved for advanced or high-risk disease.
Role of Radiotherapy: 53% supported combined modality treatment in early-stage disease; others (47%) preferred PET-adapted approaches to avoid radiation toxicity.
Targeted Therapy: Brentuximab Vedotin and anti-PD-1 therapies (nivolumab, pembrolizumab) were discussed, especially for refractory patients. 58% showed optimism, while 42% highlighted cost or access issues.
Follow-Up (10% of physician discussions)
PET Surveillance and Deauville Criteria: Used to assess treatment response. 67% of discussions supported PET-based follow-up, while 33% questioned its utility in routine surveillance post-remission.
Monitoring for Late Effects: Fertility, cardiac, and secondary malignancy follow-up plans were discussed. 38% of these discussions advocated for structured survivorship care, while 62% noted inconsistency or lack of resources.
.png)
Geographical Analysis of Physician Discussions on Hodgkin’s Lymphoma

Of the 65 countries analyzed, the following topics were discussed in prominent countries:
· United States
o Frequent discussion of checkpoint inhibitors and Brentuximab Vedotin.
o Emphasis on balancing cost with clinical benefit in relapsed cases.
· United Kingdom
o Preference for PET-guided treatment protocols and concern about overuse of BEACOPP.
· Germany
o Active discussions on prognostic scoring systems and Deauville interpretation.
o Structured approaches to risk-adapted treatment were often referenced.
· France
o Focused on minimizing long-term toxicity and fertility counseling for younger patients.
· Italy
o Expressed confidence in traditional ABVD-based protocols and discussed national treatment guidelines.
· Spain
o Highlighted concerns over delayed diagnosis and inconsistent access to advanced treatments.
· Canada
o Prominent discussions on survivorship care and access to supportive services.
Cross-Country Differences in Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Discussions
This section highlights dimensions where physician discussions diverged across countries.
1. Targeted Therapy Adoption vs. Traditional Chemotherapy Preference
This theme contrasts discussions focused on modern therapies (e.g., Brentuximab, checkpoint inhibitors) versus those favoring established regimens (e.g., ABVD, BEACOPP).
Targeted Therapy Emphasis:
Brazil and the United States led discussions around immunotherapy and targeted agents, with Italy and Israel also showing notable engagement with newer treatment modalities.
Traditional Chemotherapy Emphasis:
Seen most in Spain and Mexico, where ABVD and BEACOPP were discussed as standard frontline options.
2. Standardized vs. Personalized Follow-Up Practices
This theme contrasts countries where physicians reported using structured PET-based protocols with those favoring or describing limited, case-by-case follow-up.
Standardized PET Surveillance:
Most emphasized in Spain, Turkey, and Brazil, reflecting broad reliance on PET scans for monitoring treatment response or remission.
Personalized Follow-Up:
Poland and the United States physicians mentioned personalized follow-up planning, though overall this was not a major theme.
.png)
Engagement Recommendations:

As can be seen from the report, there are some knowledge gaps on the topic of Hodgkin’s lymphoma, especially surrounding emerging frontline regimens. An awareness campaign could be beneficial in this case.
G-Med's Awareness Package could be a good fit here.



.png)